在上一篇文章中我们谈论了Model View Presenter (MVP)的概念和在Android开发中的优点。这是系列文章的第二篇,我们来动手实践一下,将使用典型的形式实现一个MVP结构,不使用任何Android SDK或JAVA以外的库。
我们会开发一个简单的工程,但是由于涉及大量的对象,可能使项目看起来有些复杂。但是,一旦你掌握了,你就会明白MVP模式如何能帮助你。如果你想直接看代码,在这里。
Presenter
Presenter是View和Model的中间人。它从Model层获取数据,格式化后返回给View层。 但是和典型的MVC模式不同的是,它还决定如何处理你和视图的交互。
View
视图层,通常是由Activity实现,其中包含有presenter的引用。视图层唯一要做的事就是响应 用户的操作,调用Presenter层的方法。
Model
在有良好分层结构的应用中,Model层只是domain层或者业务逻辑的入口。把它看做视图层 数据的提供者就好。
以上优秀的定义提取自Antonio Leiva’s article
使用MVP模式的最大任务是增加我们项目的关注分离.因此我们需要确保Model层,View层和Presenter层的隔离。这种情况下,View层和Model层无法直接通信,因此Presenter负责各层的通讯
让我们设想一个简单的应用,它允许用户在旅途中做笔记。主要就是用户记录笔记,系统保存和展示数据。如果我们沿着输入笔记的行为,结合MVP模式,我们会得到下图:
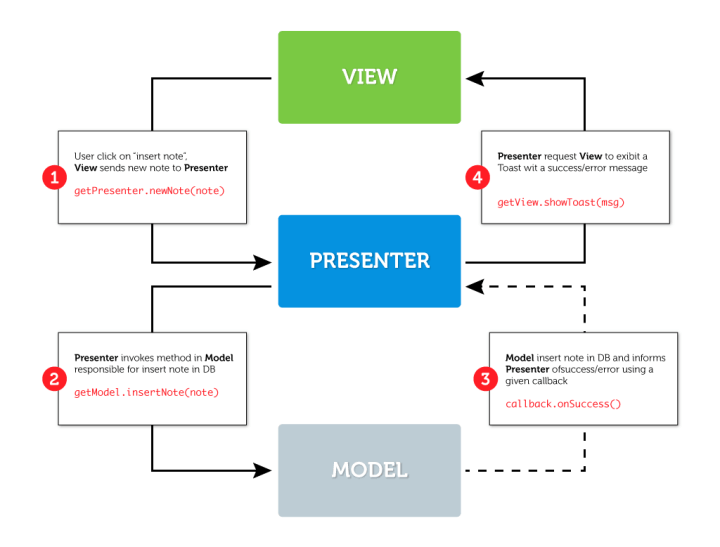
这个映射给了我们对类设计的灵感。上述不同层之间的通信过程实现可能会不一样:直接调用对象的方法,使用接口或者使用EventBus。然而,既然我们的实现方式遵循典型方式,并且意在增加关注分离,所以我们只用原始简单的接口。
让我们根据上面的行为图来构造我们的MVP模式类图。我们会对概念做一点改动,把callback换成interface,来将结果从Model层传回Presenter层。我相信这种方式更高效,但是有人会对此有争议,认为callback会增加关注分离。
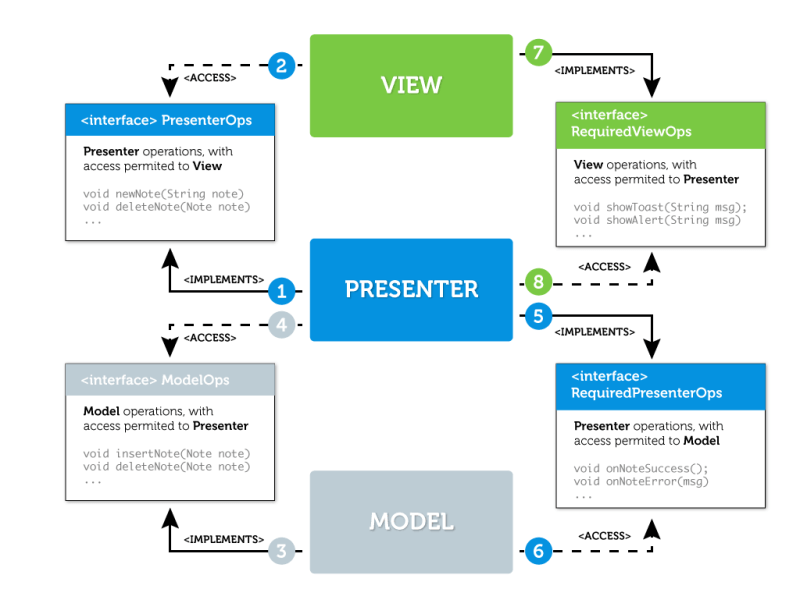
事不宜迟,让我们动起来!先定义操作。为了更好的结构组织,我们使用一个“umbrella”类,包含所有层次间通讯的接口。
注意:由于实现MVP模式已经很复杂了,我不会实现其他多余的内容。我假设读者都对Android SDK有很好的理解,因此不需要我关注这些。
/*
* Aggregates all communication operations between MVP pattern layer:
* Model, View and Presenter
*/
public interface MainMVP {
/**
* View mandatory methods. Available to Presenter
* Presenter -> View
*/
interface RequiredViewOps {
void showToast(String msg);
void showAlert(String msg);
// any other ops
}
/**
* Operations offered from Presenter to View
* View -> Presenter
*/
interface PresenterOps {
void onConfigurationChanged(RequiredViewOps view);
void onDestroy(boolean isChangingConfig);
void novaNota(String textoNota);
void deletaNota(Nota nota);
// any other ops to be called from View
}
/**
* Operations offered from Presenter to Model
* Model -> Presenter
*/
interface RequiredPresenterOps {
void onNotaInserida(Nota novaNota);
void onNotaRemovida(Nota notaRemovida);
void onError(String errorMsg);
// Any other returning operation Model -> Presenter
}
/**
* Model operations offered to Presenter
* Presenter -> Model
*/
interface ModelOps {
void insereNota(Nota nota);
void removeNota(Nota nota);
void onDestroy();
// Any other data operation
}
}public class MainPresenter implements MainMVP.RequiredPresenterOps, MainMVP.PresenterOps {
// Layer View reference
private WeakReference<MainMVP.RequiredViewOps> mView;
// Layer Model reference
private MainMVP.ModelOps mModel;
// Configuration change state
private boolean mIsChangingConfig;
public MainPresenter(MainMVP.RequiredViewOps mView) {
this.mView = new WeakReference<>(mView);
this.mModel = new MainModel(this);
}
/**
* Sent from Activity after a configuration changes
* @param view View reference
*/
@Override
public void onConfigurationChanged(MainMVP.RequiredViewOps view) {
mView = new WeakReference<>(view);
}
/**
* Receives {@link MainActivity#onDestroy()} event
* @param isChangingConfig Config change state
*/
@Override
public void onDestroy(boolean isChangingConfig) {
mView = null;
mIsChangingConfig = isChangingConfig;
if ( !isChangingConfig ) {
mModel.onDestroy();
}
}
/**
* Called by user interaction from {@link MainActivity}
* creates a new Note
*/
@Override
public void newNote(String noteText) {
Note note = new Note();
note.setText(textoNota);
note.setDate(getDate());
mModel.insertNote(note);
}
/**
* Called from {@link MainActivity},
* Removes a Note
*/
@Override
public void removeNote(Note note) {
mModel.removeNote(note);
}
/**
* Called from {@link MainModel}
* when a Note is inserted successfully
*/
@Override
public void onNoteInsert(Note newNote) {
mView.get().showToast("New register added at " + newNote.getDate());
}
/**
* Receives call from {@link MainModel}
* when Note is removed
*/
@Override
public void onNoteRemoved(Note noteRemoved) {
mView.get().showToast("Note removed);
}
/**
* receive errors
*/
@Override
public void onError(String errorMsg) {
mView.get().showAlert(errorMsg);
}
}public class MainModel implements MainMVP.ModelOps {
// Presenter reference
private MainMVP.RequiredPresenterOps mPresenter;
public MainModel(MainMVP.RequiredPresenterOps mPresenter) {
this.mPresenter = mPresenter;
}
/**
* Sent from {@link MainPresenter#onDestroy(boolean)}
* Should stop/kill operations that could be running
* and aren't needed anymore
*/
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
// destroying actions
}
// Insert Note in DB
@Override
public void insertNote(Note note) {
// data business logic
// ...
mPresenter.onNoteInserted(note);
}
// Removes Note from DB
@Override
public void removeNote(Note note) {
// data business logic
// ...
mPresenter.onNoteRemoved(note);
}
}在我们的MVP模式中,视图层负责创建Presenter层,Presenter层负责实例化Model层对象。考虑到使用Activity来实现View层,我们需要考虑一些Android的细节,尤其是销毁和创建activities及其对象的生命周期。
这就是说,我们需要增加第四个元素StateMaintainer,负责在生命周期的变化中维护Presenter和Model的状态。使用retained fragment来实现这个对象,如下是一个简化的MVP模式Activity生命周期:
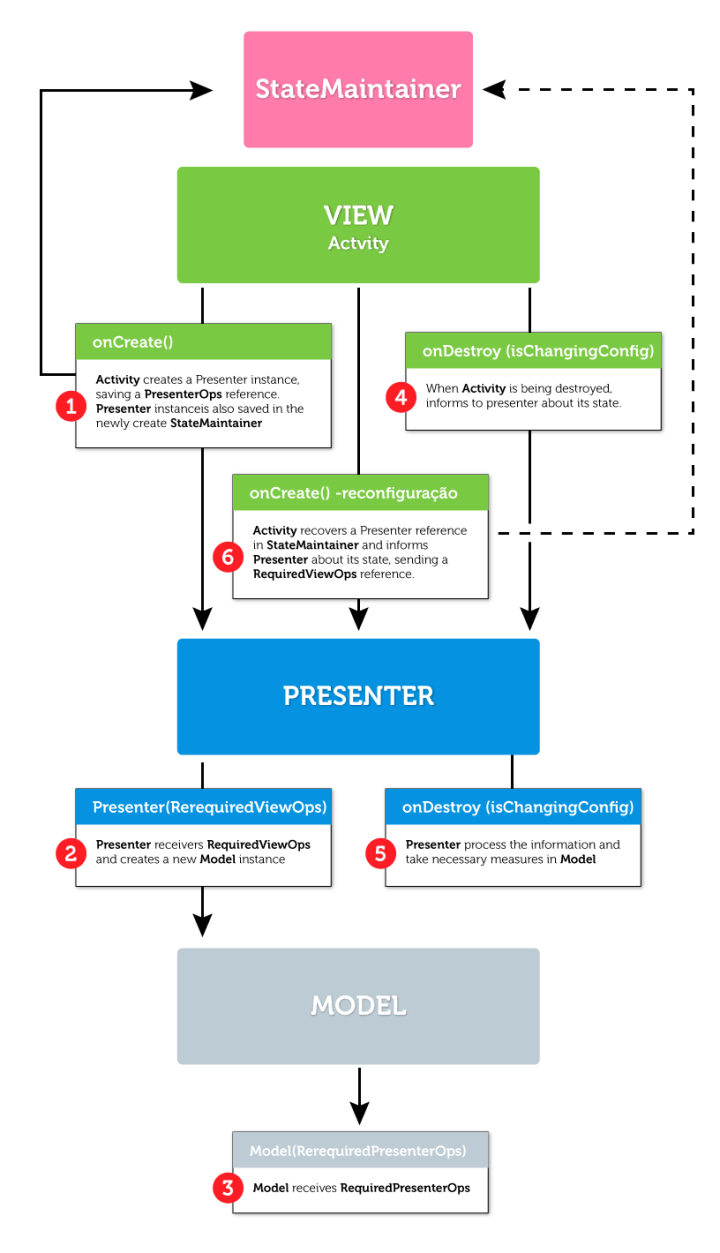
StateMaintainer的这种实现可以用来存储任何对象的状态。
StateMainainer
public class StateMaintainer {
protected final String TAG = getClass().getSimpleName();
private final String mStateMaintenerTag;
private final WeakReference<FragmentManager> mFragmentManager;
private StateMngFragment mStateMaintainerFrag;
/**
* Constructor
* @param fragmentManager FragmentManager reference
* @param stateMaintainerTAG the TAG used to insert the state maintainer fragment
*/
public StateMaintainer(FragmentManager fragmentManager, String stateMaintainerTAG) {
mFragmentManager = new WeakReference<>(fragmentManager);
mStateMaintenerTag = stateMaintainerTAG;
}
/**
* Create the state maintainer fragment
* @return true: the frag was created for the first time
* false: recovering the object
*/
public boolean firstTimeIn() {
try {
// Recovering the reference
mStateMaintainerFrag = (StateMngFragment)mFragmentManager.get().findFragmentByTag(mStateMaintenerTag);
// Creating a new RetainedFragment
if (mStateMaintainerFrag == null) {
Log.d(TAG, "Creating a new RetainedFragment " + mStateMaintenerTag);
mStateMaintainerFrag = new StateMngFragment();
mFragmentManager.get().beginTransaction()
.add(mStateMaintainerFrag,mStateMaintenerTag).commit();
return true;
} else {
Log.d(TAG, "Returns a existent retained fragment existente " + mStateMaintenerTag);
return false;
}
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
Log.w(TAG, "Error firstTimeIn()");
return false;
}
}
/**
* Insert Object to be preserved during configuration change
* @param key Object's TAG reference
* @param obj Object to maintain
*/
public void put(String key, Object obj) {
mStateMaintainerFrag.put(key, obj);
}
/**
* Insert Object to be preserved during configuration change
* Uses the Object's class name as a TAG reference
* Should only be used one time by type class
* @param obj Object to maintain
*/
public void put(Object obj) {
put(obj.getClass().getName(), obj);
}
/**
* Recovers saved object
* @param key TAG reference
* @param <T> Class type
* @return Objects
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T get(String key) {
return mStateMaintainerFrag.get(key);
}
/**
* Verify the object existence
* @param key Obj TAG
*/
public boolean hasKey(String key) {
return mStateMaintainerFrag.get(key) != null;
}
/**
* Save and manages objects that show be preserved
* during configuration changes.
*/
public static class StateMngFragment extends Fragment {
private HashMap<String, Object> mData = new HashMap<>();
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// Grants that the frag will be preserved
setRetainInstance(true);
}
/**
* Insert objects
* @param key reference TAG
* @param obj Object to save
*/
public void put(String key, Object obj) {
mData.put(key, obj);
}
/**
* Insert obj using class name as TAG
* @param object obj to save
*/
public void put(Object object) {
put(object.getClass().getName(), object);
}
/**
* Recover obj
* @param key reference TAG
* @param <T> Class
* @return Obj saved
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T get(String key) {
return (T) mData.get(key);
}
}
}public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements MainMVP.RequiredViewOps {
protected final String TAG = getClass().getSimpleName();
// Responsible to maintain the Objects state
// during changing configuration
private final StateMaintainer mStateMaintainer = new StateMaintainer( this.getFragmentManager(), TAG );
// Presenter operations
private MainMVP.PresenterOps mPresenter;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
startMVPOps();
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Toolbar toolbar = (Toolbar) findViewById(R.id.toolbar);
setSupportActionBar(toolbar);
FloatingActionButton fab = (FloatingActionButton)findViewById(R.id.fab);
}
/**
* Initialize and restart the Presenter.
* This method should be called after {@link Activity#onCreate(Bundle)}
*/
public void startMVPOps() {
try {
if ( mStateMaintainer.firstTimeIn() ) {
Log.d(TAG, "onCreate() called for the first time");
initialize(this);
} else {
Log.d(TAG, "onCreate() called more than once");
reinitialize(this);
}
} catch ( InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException e ) {
Log.d(TAG, "onCreate() " + e );
throw new RuntimeException( e );
}
}
/**
* Initialize relevant MVP Objects.
* Creates a Presenter instance, saves the presenter in {@link StateMaintainer}
*/
private void initialize( MainMVP.RequiredViewOps view ) throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException{
mPresenter = new MainPresenter(view);
mStateMaintainer.put(MainMVP.PresenterOps.class.getSimpleName(), mPresenter);
}
/**
* Recovers Presenter and informs Presenter that occurred a config change.
* If Presenter has been lost, recreates a instance
*/
private void reinitialize( MainMVP.RequiredViewOps view)
throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
mPresenter = mStateMaintainer.get( MainMVP.PresenterOps.class.getSimpleName() );
if ( mPresenter == null ) {
Log.w(TAG, "recreating Presenter");
initialize( view );
} else {
mPresenter.onConfigurationChanged( view );
}
}
// Show AlertDialog
@Override
public void showAlert(String msg) {
// show alert Box
}
// Show Toast
@Override
public void showToast(String msg) {
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), msg, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show;
}
}我知道这篇文章有一点长了,很抱歉。但我真的希望可以帮到谁。下一遍文章,我们会讨论如何使用最终的框架,它包含了一些可以加快MVP实现的抽象,我们也会谈论一些适配的小问题。
回头见!
京东创始人刘强东和其妻子章泽天最近成为了互联网舆论关注的焦点。有关他们“移民美国”和在美国购买豪宅的传言在互联网上广泛传播。然而,京东官方通过微博发言人发布的消息澄清了这些传言,称这些言论纯属虚假信息和蓄意捏造。
日前,据博主“@超能数码君老周”爆料,国内三大运营商中国移动、中国电信和中国联通预计将集体采购百万台规模的华为Mate60系列手机。
据报道,荷兰半导体设备公司ASML正看到美国对华遏制政策的负面影响。阿斯麦(ASML)CEO彼得·温宁克在一档电视节目中分享了他对中国大陆问题以及该公司面临的出口管制和保护主义的看法。彼得曾在多个场合表达了他对出口管制以及中荷经济关系的担忧。
今年早些时候,抖音悄然上线了一款名为“青桃”的 App,Slogan 为“看见你的热爱”,根据应用介绍可知,“青桃”是一个属于年轻人的兴趣知识视频平台,由抖音官方出品的中长视频关联版本,整体风格有些类似B站。
日前,威马汽车首席数据官梅松林转发了一份“世界各国地区拥车率排行榜”,同时,他发文表示:中国汽车普及率低于非洲国家尼日利亚,每百户家庭仅17户有车。意大利世界排名第一,每十户中九户有车。
近日,一项新的研究发现,维生素 C 和 E 等抗氧化剂会激活一种机制,刺激癌症肿瘤中新血管的生长,帮助它们生长和扩散。
据媒体援引消息人士报道,苹果公司正在测试使用3D打印技术来生产其智能手表的钢质底盘。消息传出后,3D系统一度大涨超10%,不过截至周三收盘,该股涨幅回落至2%以内。
9月2日,坐拥千万粉丝的网红主播“秀才”账号被封禁,在社交媒体平台上引发热议。平台相关负责人表示,“秀才”账号违反平台相关规定,已封禁。据知情人士透露,秀才近期被举报存在违法行为,这可能是他被封禁的部分原因。据悉,“秀才”年龄39岁,是安徽省亳州市蒙城县人,抖音网红,粉丝数量超1200万。他曾被称为“中老年...
9月3日消息,亚马逊的一些股东,包括持有该公司股票的一家养老基金,日前对亚马逊、其创始人贝索斯和其董事会提起诉讼,指控他们在为 Project Kuiper 卫星星座项目购买发射服务时“违反了信义义务”。
据消息,为推广自家应用,苹果现推出了一个名为“Apps by Apple”的网站,展示了苹果为旗下产品(如 iPhone、iPad、Apple Watch、Mac 和 Apple TV)开发的各种应用程序。
特斯拉本周在美国大幅下调Model S和X售价,引发了该公司一些最坚定支持者的不满。知名特斯拉多头、未来基金(Future Fund)管理合伙人加里·布莱克发帖称,降价是一种“短期麻醉剂”,会让潜在客户等待进一步降价。
据外媒9月2日报道,荷兰半导体设备制造商阿斯麦称,尽管荷兰政府颁布的半导体设备出口管制新规9月正式生效,但该公司已获得在2023年底以前向中国运送受限制芯片制造机器的许可。
近日,根据美国证券交易委员会的文件显示,苹果卫星服务提供商 Globalstar 近期向马斯克旗下的 SpaceX 支付 6400 万美元(约 4.65 亿元人民币)。用于在 2023-2025 年期间,发射卫星,进一步扩展苹果 iPhone 系列的 SOS 卫星服务。
据报道,马斯克旗下社交平台𝕏(推特)日前调整了隐私政策,允许 𝕏 使用用户发布的信息来训练其人工智能(AI)模型。新的隐私政策将于 9 月 29 日生效。新政策规定,𝕏可能会使用所收集到的平台信息和公开可用的信息,来帮助训练 𝕏 的机器学习或人工智能模型。
9月2日,荣耀CEO赵明在采访中谈及华为手机回归时表示,替老同事们高兴,觉得手机行业,由于华为的回归,让竞争充满了更多的可能性和更多的魅力,对行业来说也是件好事。
《自然》30日发表的一篇论文报道了一个名为Swift的人工智能(AI)系统,该系统驾驶无人机的能力可在真实世界中一对一冠军赛里战胜人类对手。
近日,非营利组织纽约真菌学会(NYMS)发出警告,表示亚马逊为代表的电商平台上,充斥着各种AI生成的蘑菇觅食科普书籍,其中存在诸多错误。
社交媒体平台𝕏(原推特)新隐私政策提到:“在您同意的情况下,我们可能出于安全、安保和身份识别目的收集和使用您的生物识别信息。”
2023年德国柏林消费电子展上,各大企业都带来了最新的理念和产品,而高端化、本土化的中国产品正在不断吸引欧洲等国际市场的目光。
罗永浩日前在直播中吐槽苹果即将推出的 iPhone 新品,具体内容为:“以我对我‘子公司’的了解,我认为 iPhone 15 跟 iPhone 14 不会有什么区别的,除了序(列)号变了,这个‘不要脸’的东西,这个‘臭厨子’。