一、意图
运用共享技术有效的支持大量细粒度的对象
享元模式变化的是对象的存储开销
二、享元模式结构图
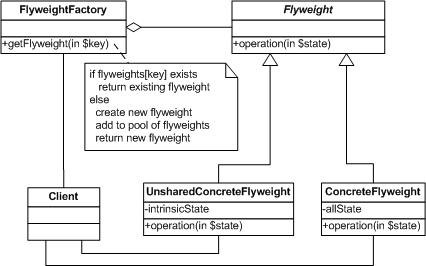
三、享元模式中主要角色
**抽象享元(Flyweight)角色:此角色是所有的具体享元类的超类,为这些类规定出需要实现的公共接口。那些需要外蕴状态的操作可以通过调用商业以参数形式传入
具体享元(ConcreteFlyweight)角色:实现Flyweight接口,并为内部状态(如果有的话)拉回存储空间。ConcreteFlyweight对象必须是可共享的。它所存储的状态必须是内部的
不共享的具体享元(UnsharedConcreteFlyweight)角色:并非所有的Flyweight子类都需要被共享。Flyweigth使共享成为可能,但它并不强制共享。
享元工厂(FlyweightFactory)角色:负责创建和管理享元角色。本角色必须保证享元对象可能被系统适当地共享
客户端(Client)角色:本角色需要维护一个对所有享元对象的引用。本角色需要自行存储所有享元对象的外部状态
四、享元模式的优点和缺点
享元模式的优点:Flyweight模式可以大幅度地降低内存中对象的数量。
享元模式的缺点:
1、Flyweight模式使得系统更加复杂
2、Flyweigth模式将享元对象的状态外部化,而读取外部状态使得运行时间稍微变长
五、享元模式适用场景
当以下情况都成立时使用Flyweight模式:
1、一个应用程序使用了大量的对象
2、完全由于使用大量的对象,造成很大的存储开销
3、对象的大多数状态都可变为外部状态
4、如果删除对象的外部状态,那么可以用相对较少的共享对象取代很多组对象
5、应用程序不依赖于对象标识。
六、享元模式与其它模式
单例模式(Singleton):客户端要引用享元对象,是通过工厂对象创建或者获得的,客户端每次引用一个享元对象,都是可以通过同一个工厂对象来引用所需要的享元对象。因此,可以将享元工厂设计成单例模式,这样就可以保证客户端只引用一个工厂实例。因为所有的享元对象都是由一个工厂对象统一管理的,所以在客户端没有必要引用多个工厂对象。不管是单纯享元模式还是复合享元模式中的享元工厂角色,都可以设计成为单例模式,对于结果是不会有任何影响的。
Composite模式:复合享元模式实际上是单纯享元模式与合成模式的组合。单纯享元对象可以作为树叶对象来讲,是可以共享的,而复合享元对象可以作为树枝对象,因此在复合享元角色中可以添加聚集管理方法。
七、享元模式PHP示例
**
<?php
/**
* 抽象享元角色
*/
abstract class Flyweight {
/**
* 示意性方法
* @param string $state 外部状态
*/
abstract public function operation($state);
}
/**
* 具体享元角色
*/
class ConcreteFlyweight extends Flyweight {
private $_intrinsicState = null;
/**
* 构造方法
* @param string $state 内部状态
*/
public function __construct($state) {
$this->_intrinsicState = $state;
}
public function operation($state) {
echo 'ConcreteFlyweight operation, Intrinsic State = ' . $this->_intrinsicState
. ' Extrinsic State = ' . $state . '<br />';
}
}
/**
* 不共享的具体享元,客户端直接调用
*/
class UnsharedConcreteFlyweight extends Flyweight {
private $_intrinsicState = null;
/**
* 构造方法
* @param string $state 内部状态
*/
public function __construct($state) {
$this->_intrinsicState = $state;
}
public function operation($state) {
echo 'UnsharedConcreteFlyweight operation, Intrinsic State = ' . $this->_intrinsicState
. ' Extrinsic State = ' . $state . '<br />';
}
}
/**
* 享元工厂角色
*/
class FlyweightFactory {
private $_flyweights;
public function __construct() {
$this->_flyweights = array();
}
public function getFlyweigth($state) {
if (isset($this->_flyweights[$state])) {
return $this->_flyweights[$state];
} else {
return $this->_flyweights[$state] = new ConcreteFlyweight($state);
}
}
}
/**
* 客户端
*/
class Client {
/**
* Main program.
*/
public static function main() {
$flyweightFactory = new FlyweightFactory();
$flyweight = $flyweightFactory->getFlyweigth('state A');
$flyweight->operation('other state A');
$flyweight = $flyweightFactory->getFlyweigth('state B');
$flyweight->operation('other state B');
/* 不共享的对象,单独调用 */
$uflyweight = new UnsharedConcreteFlyweight('state A');
$uflyweight->operation('other state A');
}
}
Client::main();
?>
八、复合享元模式
复合享元模式对象是由一些单纯享元使用合成模式加以复合而成
复合享元角色所代表的对象是不可以共享的,但是一个复合享元对象可以分解成为多个本身是单纯享元对象的组合。
九、复合享元模式PHP示例
<?php
/**
* 抽象享元角色
*/
abstract class Flyweight {
/**
* 示意性方法
* @param string $state 外部状态
*/
abstract public function operation($state);
}
/**
* 具体享元角色
*/
class ConcreteFlyweight extends Flyweight {
private $_intrinsicState = null;
/**
* 构造方法
* @param string $state 内部状态
*/
public function __construct($state) {
$this->_intrinsicState = $state;
}
public function operation($state) {
echo 'ConcreteFlyweight operation, Intrinsic State = ' . $this->_intrinsicState
. ' Extrinsic State = ' . $state . '<br />';
}
}
/**
* 不共享的具体享元,客户端直接调用
*/
class UnsharedConcreteFlyweight extends Flyweight {
private $_flyweights;
/**
* 构造方法
* @param string $state 内部状态
*/
public function __construct() {
$this->_flyweights = array();
}
public function operation($state) {
foreach ($this->_flyweights as $flyweight) {
$flyweight->operation($state);
}
}
public function add($state, Flyweight $flyweight) {
$this->_flyweights[$state] = $flyweight;
}
}
/**
* 享元工厂角色
*/
class FlyweightFactory {
private $_flyweights;
public function __construct() {
$this->_flyweights = array();
}
public function getFlyweigth($state) {
if (is_array($state)) { // 复合模式
$uFlyweight = new UnsharedConcreteFlyweight();
foreach ($state as $row) {
$uFlyweight->add($row, $this->getFlyweigth($row));
}
return $uFlyweight;
} else if (is_string($state)) {
if (isset($this->_flyweights[$state])) {
return $this->_flyweights[$state];
} else {
return $this->_flyweights[$state] = new ConcreteFlyweight($state);
}
} else {
return null;
}
}
}
/**
* 客户端
*/
class Client {
/**
* Main program.
*/
public static function main() {
$flyweightFactory = new FlyweightFactory();
$flyweight = $flyweightFactory->getFlyweigth('state A');
$flyweight->operation('other state A');
$flyweight = $flyweightFactory->getFlyweigth('state B');
$flyweight->operation('other state B');
/* 复合对象*/
$uflyweight = $flyweightFactory->getFlyweigth(array('state A', 'state B'));
$uflyweight->operation('other state A');
}
}
Client::main();
?>十、PHP中享元模式的地位
相对于其它模式,Flyweight模式在PHP的现有版本中没有太大的意义,因为PHP的生命周期是页面级的,即从一个PHP文件执行开始会载入所需的资源,当执行完毕后,这些所有的资源会被全部释放,而一般来说我们也不会让一个页面执行太长时间。
以上就是使用php实现享元模式的代码,还有一些关于享元模式的概念区分,希望对大家的学习有所帮助。