C/C++面向WebAssembly编程
3.5 Module定制及其他
JavaScript对象Module控制了运行时相关的很多行为。在之前的章节中,我们尝试了:
- 使用
Module.onRuntimeInitialized回调在运行时准备就绪后执行测试代码。 - 通过更改
Module.TOTAL_MEMORY设置内存容量。
我们可以使用类似的方法更改Module的标准输出行为,例如:
<!--custom_print.html-->
<script>
Module = {};
Module.print = function(e) {
alert(e);
}
</script>
<script src="hello.js"></script>上述代码将Module.print的更改为使用alert()函数弹出提示框,上述页面载入1.2节的helloworld例程的.js文件后,输出如下:
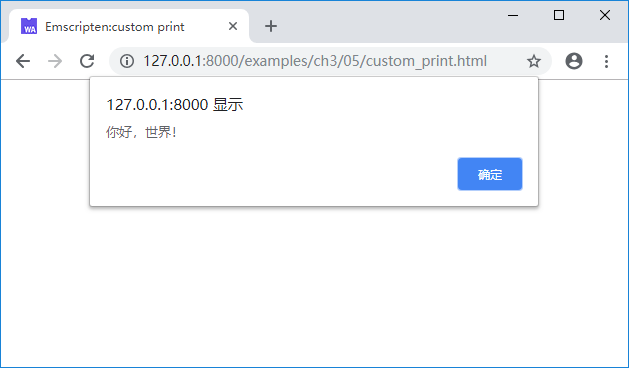
除此之外,Module对象中提供了Module.arguments、Module.onAbort、Module.noInitialRun等一系列可自定义的对象/方法,具体使用详见Emscripten官方文档https://kripken.github.io/emscripten-site/docs/api_reference/module.html。
在某些情况下,我们希望在Emscripten生成的.js胶水代码的前后分别插入一些自定义代码(比如在其前部插入C/C++代码将要调用的JavaScript方法、设置Module自定义参数等),此时可以使用两个特殊的编译参数:--pre-js <file>与--post-js <file>。
例如hello.cc如下:
//hello.cc
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
printf("你好,世界!\n");
return 0;
}pre.js如下:
//pre.js
Module = {};
Module.print = function(e) {
console.log('pre.js: ', e);
}post.js如下:
//post.js
console.log('post.js');使用下列命令编译:
emcc hello.cc --pre-js pre.js --post-js post.js -o pre_hello_post.js生成的pre_hello_post.js部分内容截取如下:
...
// --pre-jses are emitted after the Module integration code, so that they can
// refer to Module (if they choose; they can also define Module)
Module = {};
Module.print = function(e) {
console.log('pre.js: ', e);
}
// Sometimes an existing Module object exists with properties
// meant to overwrite the default module functionality. Here
// we collect those properties and reapply _after_ we configure
// the current environment's defaults to avoid having to be so
// defensive during initialization.
var moduleOverrides = {};
...
run();
// {{POST_RUN_ADDITIONS}}
// {{MODULE_ADDITIONS}}
console.log('post.js');可见其中将包含三个部分:
pre.js中的内容;hello.cc编译后产生的.js文件中的内容;post.js中的内容。
上述页面运行后输出如下:
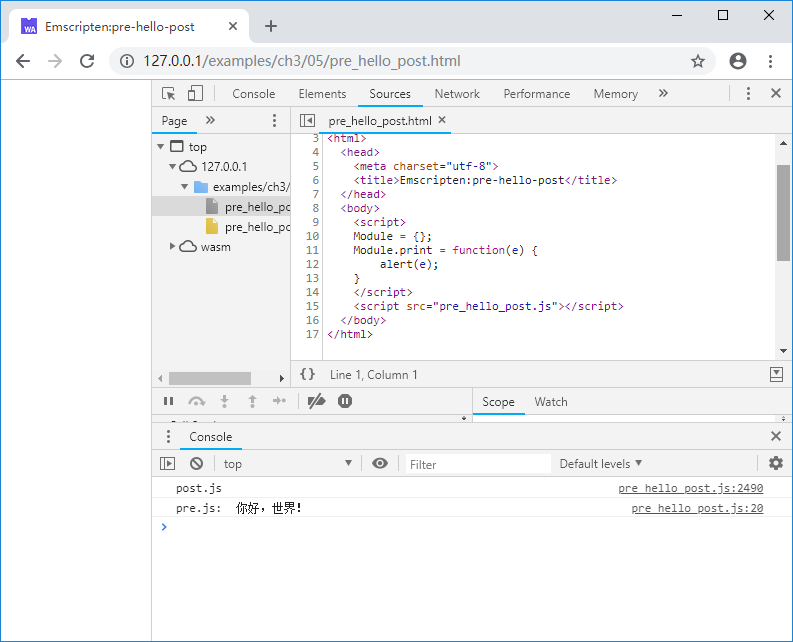
tips 注意控制台先输出了“post.js”,因为wasm模块是异步加载的。